As technology continues to evolve, heat pipe technology has emerged as a pivotal player in the realm of thermal management. It’s a fascinating world where physics and engineering intertwine, offering efficient solutions to keep electronic devices cool.
In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of heat pipe technology, exploring its principles, applications, and why it’s becoming an indispensable part of modern tech landscapes. So, buckle up and prepare for an enlightening journey into the world of heat pipe technology.
Heat Pipe Technology
Heat pipe technology traces its roots back to the mid-20th century, when George Grover, a Los Alamos National Laboratory engineer, invented it in 1963. Grover’s invention, driven by the need for effective thermal controls in the burgeoning aerospace industry, marked a revolution in heat management techniques. His original designs serve as the foundational basis for modern heat pipes, lending credibility to diverse industries.
Applications of Heat Pipe Technology
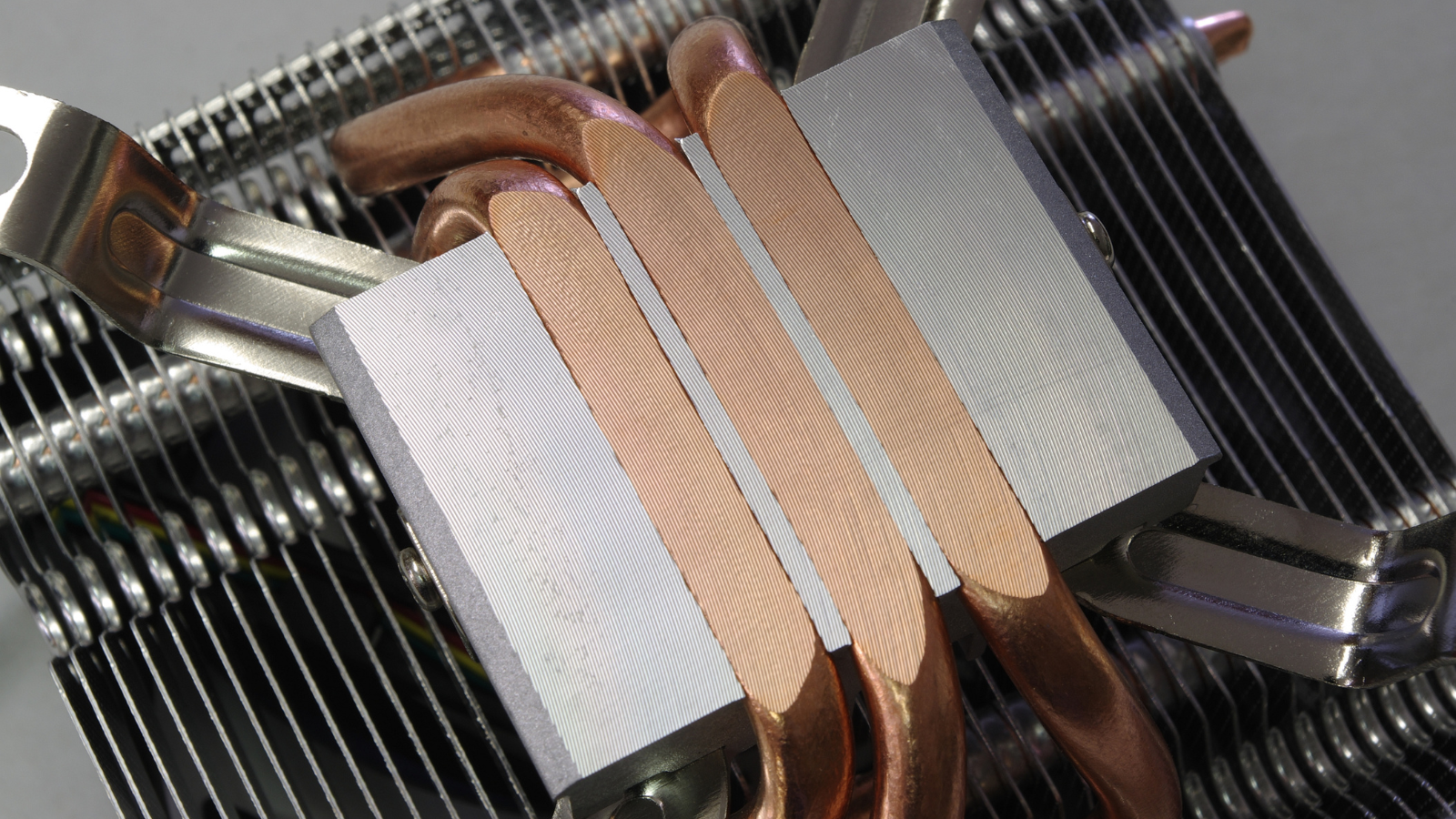
Emerging from diverse heat pipe designs are practical applications, consistently impacting and transforming various industries. Heat pipes find extensive use in electronics cooling, such as in high-performance computers and servers, drawing out the intense heat produced by CPUs. They’re also instrumental in thermal management in space vehicles, particularly in maintaining optimal temperatures for equipment and payloads. Furthermore, heat pipes play an essential role in renewable energy systems, notable in solar collectors and heat pumps. In each of these applications, the key function of heat pipes remains the controlled transfer of heat, preventing overheating and ensuring efficient thermal performance.
Advancements in Heat Pipe Technology
Enhancements in heat pipe technology continue to redefine thermal management, sparked by continuous research and innovation. Pioneers in the industry relentlessly aim at improvising heat pipe types initially covered: Thermosyphon, Variable Conductance, Diode, and Rotating heat pipes – resulting in more refined, efficient, and targeted heat management solutions.
Breaking New Ground with Nanotechnology
Researchers globally work towards redefining heat pipe technology using nanotechnology. Evidence suggests that nanofluids, when employed in heat pipes, enhance thermal conductivity significantly. For instance, researchers at Zhejiang University, in 2008, experimented with using nanofluids in heat pipes and reported thermal conductivity improvements of up to 20%.
Micro Heat Pipes: Revolutionizing Electronics Cooling
Micro heat pipes (MHPs) emerge as a groundbreaking advancement, specifically in the electronics industry. Measuring as thin as 0.5 mm, MHPs make effective thermal solutions in miniature sizes, apt for compact electronic devices. A notable example is their implementation in IBM’s ThinkPad, promoting safe thermal management.
3D Printed Heat Pipes: the Future of Personalized Thermal Solutions

3D printing technology intertwines with heat pipe technology paving the path for personalized thermal management solutions. In 2015, researchers at Purdue University demonstrated functionality of 3D printed heat pipes, showcasing their potential in offering custom-made thermal solutions for various applications.
Further evolutionary strides arrive as industry experts innovate to overcome challenges, revealing the true potential of heat pipe technology. These advancements advocate for comprehensive, efficient thermal management, and become a testament to heat pipe technology’s constant evolution amidst technological progression.
The Benefits and Limitations of Heat Pipe Technology
Heat pipe technology, despite its advancements, exhibits both pros and cons. The benefits include, but are not confined to, zero power consumption, high thermal conductivity, and the ability to operate in a wide range of temperatures. They exhibit thermal superconductivity, transferring heat more efficiently than any solid material. Aerospace applications benefit significantly from their temperature uniformity, vital in spacecraft where extremes of heat and cold exist simultaneously. Contemporary innovations, like Micro Heat Pipes, offer lightweight, compact solutions, ideal for managing heat in smaller electronic devices and aiding in miniaturization efforts.
All You Need to Know
Heat pipe technology has come a long way. It’s proven itself as a highly effective cooling method, offering impressive thermal conductivity and zero power consumption. Despite certain challenges, such as design complexities and material selection, it’s steadily advancing with innovations like nanotechnology and Micro Heat Pipes.
